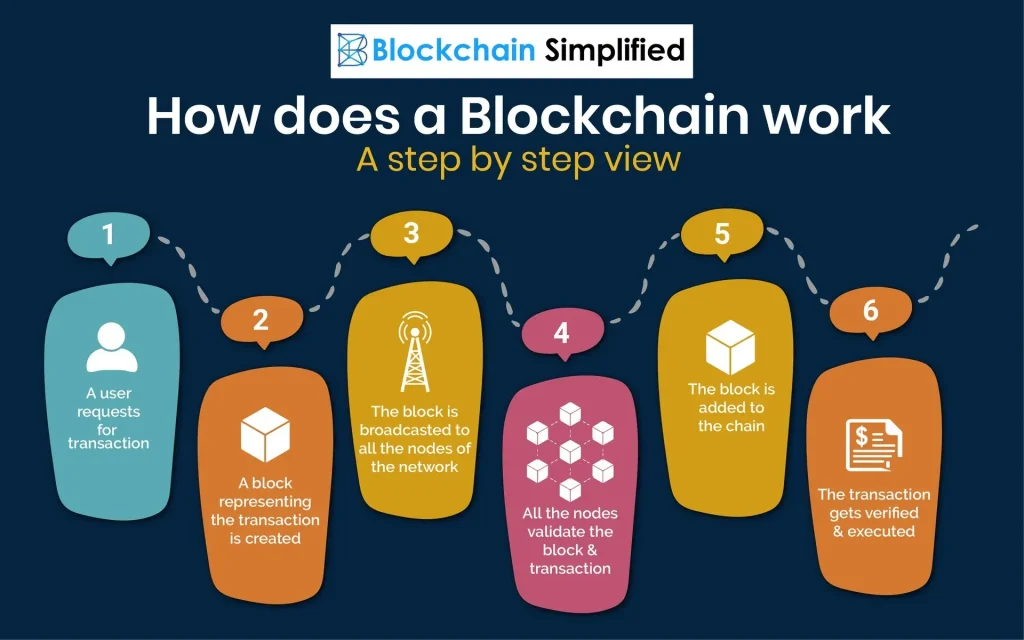
Blockchain technology has moved from a buzzword to a foundational system powering modern digital infrastructures. As a distributed ledger, it records transactions across many computers in a tamper-evident, verifiable way and supports the rise of smart contracts. Far from being limited to cryptocurrencies, the uses of blockchain technology span finance, supply chains, healthcare, identity, and governance, with decentralization in blockchain as a core benefit. This article unpacks the underlying technology, explores its uses and benefits, and includes blockchain myths debunked as a guide to separate hype from reality. By focusing on practical examples, the piece highlights what organizations can pilot today to gain trust, efficiency, and resilience.
In other terms, distributed ledger technology (DLT) or digital ledger technology describes a networked system where data is appended in tamper-evident blocks. This framing emphasizes decentralized trust, cryptographic integrity, and programmable contracts that automate processes across ecosystems. From an enterprise viewpoint, the focus is on data provenance, traceability, interoperability, and governance that scale across partners. As standards mature, emphasis shifts toward interoperability between networks, privacy by design, and scalable consensus models to support broader adoption. Ultimately, the same core idea goes by several names—DLT, distributed ledger, or crypto ledger—and under any label it aims to enable trusted collaboration without centralized control.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do smart contracts help expand the uses of blockchain technology by automating processes?
Smart contracts are self-executing code stored on the blockchain that automatically enforces terms when predefined conditions are met, removing manual steps and intermediaries. They enable faster, cheaper, auditable workflows across finance, supply chains, identity, and governance, illustrating the broad uses of blockchain technology. Because they run on a decentralized network, they support transparency, tamper-evidence, and resilience inherent to decentralization in blockchain. This combination drives efficiency gains, reduces human error, and enables new programmable business models.
What are blockchain myths debunked, and how do decentralization in blockchain and immutability address common concerns about the technology?
blockchain myths debunked show that the technology’s value goes beyond crypto to trust, provenance, and governance. Common concerns—such as energy use, speed, and regulatory fit—are being addressed through models like proof of stake, Layer-2 solutions, and governance frameworks. Decentralization in blockchain reduces single points of control, improving resilience and auditability, while immutability ensures that once records are written, they are extremely difficult to alter, supporting accountability and compliance.
| Topic | Key Points (English) |
|---|---|
| What is blockchain technology? |
|
| Why decentralization matters |
|
| Key uses of blockchain technology |
|
| Benefits of blockchain technology |
|
| Common myths about blockchain technology and the truth |
|
| Real-world examples and case studies |
|
| How to assess blockchain technology for your organization |
|
| Implementing blockchain technology: practical steps |
|
| Potential challenges to watch for |
|
| The future of blockchain technology |
|
| Conclusion |
|
Summary
Blockchain technology is reshaping how organizations design trusted, transparent, and efficient digital systems. It offers a shared, tamper-evident ledger that enables collaboration without heavy reliance on traditional intermediaries, with wide-ranging uses from finance and supply chains to healthcare and identity. By combining decentralization, transparency, immutability, and programmable logic, blockchain technology can unlock improvements in security, efficiency, and trust. A thoughtful approach to governance, security by design, and pragmatic pilots is essential to realizing practical value while navigating regulatory and interoperability challenges.